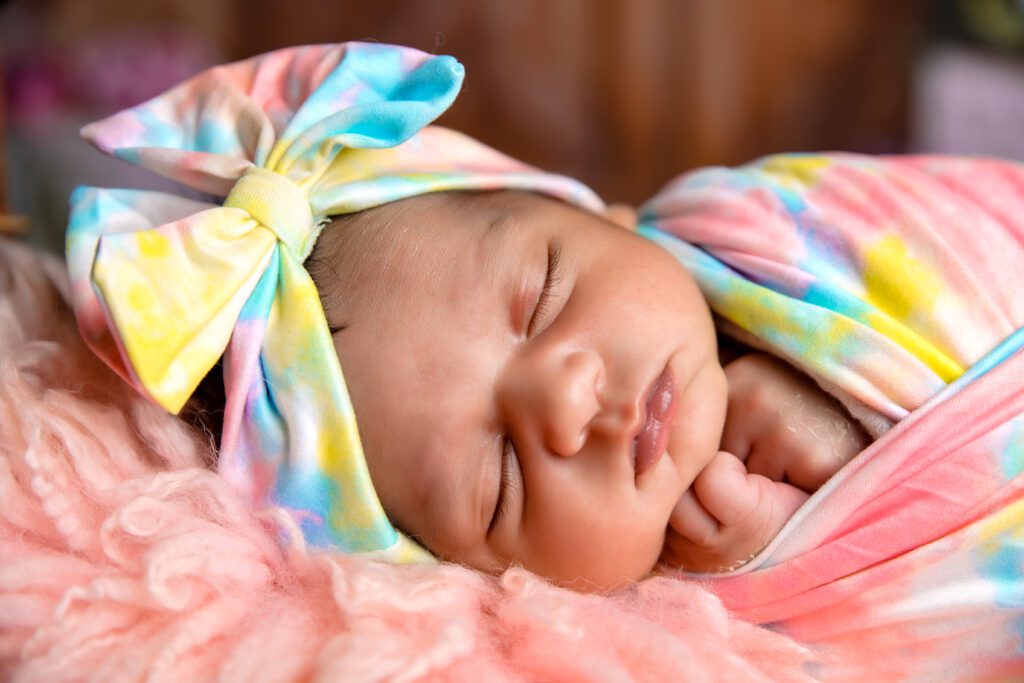
Many parents wonder why their baby buries their face when sleeping. This behavior may seem strange, but it is actually quite common and has a few possible explanations.
1. At what age do babies typically start burying their faces when sleeping?
Babies typically start burying their faces when sleeping around 3 to 4 months of age. This is a common behavior that many infants exhibit as they become more mobile and develop better control over their movements. It is important for parents to understand that this behavior is a normal part of a baby’s development and not necessarily a cause for concern.
At around 3 to 4 months, infants begin to develop the ability to roll over, which allows them to move more freely during sleep. As they explore different positions and movements, it is not uncommon for them to accidentally bury their faces into the mattress or bedding. While this may seem alarming to parents, it is generally harmless as long as the baby is able to move their head and breathe comfortably.
Factors That Influence Face Burying
- Mobility: As babies become more mobile and start rolling over, they are more likely to bury their faces while sleeping.
- Sleep Surface: The type of sleep surface can also influence face burying. Soft mattresses or loose bedding may increase the risk of suffocation if the baby’s face becomes buried.
- Sleep Position: Certain sleep positions, such as tummy sleeping, can increase the likelihood of face burying. It is generally recommended that babies sleep on their backs to reduce the risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
Tips for Safe Sleep
- Ensure a firm and flat sleep surface without any loose bedding or pillows that could pose a suffocation risk.
- Dress your baby in lightweight clothing and avoid overdressing them, which can cause overheating.
- Keep the sleeping area free from any potential hazards, such as cords or toys that could pose a strangulation risk.
- Always place your baby on their back to sleep, as this is the safest sleep position to reduce the risk of SIDS.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
If you have concerns about your baby burying their face while sleeping or if they are having difficulty breathing, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide guidance and ensure that there are no underlying medical conditions contributing to this behavior.
2. Is it normal for a baby to bury their face while sleeping?
Understanding Normal Sleep Patterns
During the early months of life, it is quite common for babies to bury their faces while sleeping. This behavior is often seen in newborns and infants who are still adjusting to life outside the womb. Babies may find comfort in snuggling their faces into soft surfaces, such as blankets or pillows, as it reminds them of the cozy environment they experienced in the womb.
The Startle Reflex
One possible reason why babies bury their faces during sleep is due to the startle reflex. This reflex causes sudden jerking movements or flailing of limbs, which can startle a baby awake. By burying their face, babies may be trying to create a sense of security and reduce the chances of being startled awake.
– It is important to note that while this behavior is generally considered normal, parents should always ensure that there are no loose blankets or pillows near the baby’s face, as these can pose suffocation risks.
– If a baby consistently buries their face deeply into surfaces and has difficulty breathing or shows signs of distress, it is advisable to consult a pediatrician for further evaluation.
3. What are the possible reasons behind a baby burying their face during sleep?
Seeking Comfort and Security
Babies have an innate need for comfort and security, especially during sleep. Burying their faces may provide them with a sense of coziness and familiarity that helps them relax and fall asleep more easily.
Mimicking Familiar Sensations
Another possible reason behind this behavior is that babies may be mimicking familiar sensations from when they were in the womb. In utero, they were surrounded by warm amniotic fluid and had limited space. Burying their faces into surfaces may recreate a similar feeling of being enclosed and secure.
– It is important for parents to create a safe sleep environment by following the guidelines recommended by pediatricians, such as placing babies on their backs to sleep and using a firm mattress without any loose bedding.
– If a baby consistently buries their face in a way that obstructs their breathing or causes distress, it is essential to seek medical advice to rule out any underlying issues.
4. How does burying the face while sleeping affect a baby’s breathing?
Effects on Oxygen Intake
When a baby buries their face while sleeping, it can potentially obstruct their airway and limit the amount of oxygen they are able to take in. This is particularly concerning for newborns who have not yet developed strong neck muscles to reposition themselves if their breathing becomes compromised. The lack of oxygen intake can lead to hypoxia, which is a condition characterized by low levels of oxygen in the body. Hypoxia can have serious consequences on a baby’s health and development.
Increase in Carbon Dioxide Levels
Burying the face while sleeping can also result in an increase in carbon dioxide levels within a baby’s immediate breathing zone. When a baby breathes out, they release carbon dioxide into the surrounding air. If their face is buried, this exhaled carbon dioxide may accumulate around them instead of dissipating properly. Breathing in high levels of carbon dioxide can be harmful and may cause symptoms such as dizziness, headaches, and even respiratory distress.
Prevention Measures
To prevent these potential risks, it is important for parents to ensure that their baby sleeps on their back with no loose bedding or objects near their face that could obstruct their breathing. Additionally, using a firm mattress and avoiding soft surfaces such as pillows or plush toys in the sleep environment can help reduce the likelihood of a baby burying their face during sleep.
5. Are there any potential risks associated with a baby burying their face during sleep?
Suffocation Risk
One of the main risks associated with a baby burying their face during sleep is suffocation. When a baby’s face is covered or pressed against bedding or other objects, it increases the risk of suffocation if they are unable to move or reposition themselves. This is especially dangerous for infants who are not yet able to roll over independently.
SIDS (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome)
Burying the face while sleeping has also been linked to an increased risk of SIDS, which is the sudden and unexplained death of an otherwise healthy baby. While the exact cause of SIDS is still unknown, certain sleep practices, including burying the face, have been identified as potential contributing factors. It is important for parents to be aware of safe sleep guidelines and take necessary precautions to reduce the risk of SIDS.
Safe Sleep Practices
To minimize the potential risks associated with a baby burying their face during sleep, it is crucial for parents to follow safe sleep practices recommended by pediatricians and organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). These practices include placing babies on their back to sleep, using a firm mattress in a crib or bassinet free from loose bedding or objects that could obstruct breathing, and ensuring a comfortable room temperature without overheating.
6. Can swaddling or using a pacifier help prevent a baby from burying their face while sleeping?
Swaddling
Swaddling can be an effective technique to help prevent babies from burying their faces while sleeping. When done correctly, swaddling securely wraps a baby in a blanket, restricting their movements and reducing the likelihood of them accidentally covering their face with bedding or blankets. However, it is important to note that swaddling should only be practiced until a baby shows signs of rolling over independently.
Pacifier Use
Using a pacifier during sleep has also been found to reduce the risk of babies burying their faces. The presence of a pacifier in a baby’s mouth can help keep their airway open and discourage them from turning their head and burying their face into bedding or other objects. However, it is essential to follow safe pacifier practices, such as using an age-appropriate pacifier and ensuring it is clean and in good condition.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
Parents should consult with their healthcare provider before implementing swaddling or introducing a pacifier to ensure these practices are appropriate for their baby’s individual needs. Additionally, regular monitoring of the baby during sleep is crucial to ensure they do not accidentally dislodge the pacifier or become entangled in swaddling blankets.
7. What strategies can parents use to ensure their baby sleeps safely even if they tend to bury their face?
Creating a Safe Sleep Environment
To ensure their baby sleeps safely even if they tend to bury their face, parents should focus on creating a safe sleep environment. This includes using a firm mattress with a fitted sheet, removing any soft bedding or pillows from the crib, and avoiding loose blankets or toys that could potentially cover the baby’s face. Additionally, it is important to keep the crib free from any potential hazards such as cords or strings that could pose a strangulation risk.
Using Safe Sleep Practices
Parents should also follow safe sleep practices to reduce the risk of suffocation or Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS). This includes placing the baby on their back for sleep, as this position has been shown to be the safest. It is important not to place the baby on their side or stomach, as this increases the likelihood of them burying their face into the mattress or bedding. Furthermore, parents should avoid co-sleeping with their baby and ensure that they have a separate sleep space that meets all safety guidelines.
List of Strategies:
– Use a firm mattress with a fitted sheet
– Remove soft bedding and pillows from the crib
– Avoid loose blankets or toys in the crib
– Keep the crib free from potential hazards such as cords or strings
– Place the baby on their back for sleep
– Avoid co-sleeping and provide a separate sleep space
8. Does the position in which a baby is placed for sleep impact whether they bury their face or not?
The position in which a baby is placed for sleep can indeed impact whether they bury their face or not. Placing babies on their back for sleep has been recommended by pediatricians and researchers as the safest sleep position. This position reduces the risk of SIDS and suffocation, as it allows for proper airflow and minimizes the chances of the baby burying their face into the bedding or mattress.
When babies are placed on their side or stomach, they have a higher likelihood of turning their head and burying their face into the sleep surface. This can increase the risk of suffocation if they are unable to move their head or reposition themselves. Therefore, it is crucial for parents to always place their baby on their back for sleep to ensure optimal safety.
Safe Sleep Position:
– Place the baby on their back for sleep
– Avoid placing them on their side or stomach
9. Are there any signs that indicate when it’s necessary to seek medical advice regarding a baby who consistently buries their face during sleep?
While occasional instances of a baby burying their face during sleep may not be cause for concern, consistent or prolonged episodes should prompt parents to seek medical advice. There are several signs that indicate when it’s necessary to consult a healthcare professional regarding this issue.
If a baby consistently buries their face during sleep and has difficulty breathing, shows signs of distress such as gasping or choking sounds, turns blue or pale, or experiences excessive sweating, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms could indicate an underlying respiratory problem or obstructive issue that requires medical intervention.
Additionally, if parents notice any changes in the baby’s behavior during wakefulness, such as excessive fatigue, poor feeding, irritability, or developmental delays, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider. These signs may suggest that the baby is not getting adequate restful sleep due to frequent episodes of burying their face.
Signs That Indicate Need for Medical Advice:
– Difficulty breathing during sleep
– Gasping or choking sounds
– Turning blue or pale
– Excessive sweating
– Changes in behavior during wakefulness (fatigue, poor feeding, irritability, developmental delays)
10. As babies grow older, do they naturally stop burying their faces when sleeping?
As babies grow older and develop better head control and mobility, they generally tend to naturally stop burying their faces when sleeping. This is because as their neck muscles strengthen and they gain more control over their movements, they are able to adjust their position during sleep to ensure proper breathing and comfort.
Around the age of 4 to 6 months, many babies start rolling over independently. This milestone allows them to change positions during sleep if they find themselves with their face buried into the bedding or mattress. By this stage, most babies have also developed the ability to turn their heads from side to side, further reducing the risk of suffocation or obstruction.
However, it is important for parents to continue practicing safe sleep habits even as babies grow older. Placing them on their back for sleep until at least one year of age and ensuring a safe sleep environment will help maintain a secure sleeping routine that promotes optimal safety and healthy development.
Developmental Milestones:
– Around 4 to 6 months: Independent rolling over
– Ability to change positions during sleep
– Improved head control and mobility
In conclusion, babies may bury their faces when sleeping as a natural self-soothing mechanism or to feel more secure and protected. However, it is important for parents to ensure a safe sleep environment and monitor their baby’s positioning to prevent any potential risks.
Why does my baby keep nuzzling his head?
Self-soothing is a behavior where babies find comfort by gently moving their head from side to side. They may do this when they are overwhelmed, anxious, or attempting to fall asleep. This self-soothing action is harmless and can help babies feel more at ease in unfamiliar circumstances.
Why do babies rub blankets on their face?
When a baby is securely attached to their blanket or stuffed animal, they can use it to comfort themselves and go back to sleep without needing their parents. They may snuggle with it, smell it, rub it on their face, or suck on it as a way of self-soothing.
Why do babies cover their face with their hands?
Shelley suggests that covering the eyes, face, or ears with their hands can have various interpretations, such as a child using it as a coping mechanism to block out excessive sensory input, regulate themselves, or express feelings of fear or anxiety. This action can serve multiple purposes depending on the situation.
Why does my baby like to smother himself?
They do it to reduce sensory input and feel secure, especially when they are unable to close their eyes properly. My 21-month-old child still does it with their stuffed animal toy.
What is silent reflux in babies symptoms?
Infants who experience spitting up and show signs of irritability can be easily diagnosed with reflux, but there are others who don’t spit up at all. This is known as silent reflux. Babies with silent reflux may show other symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), such as fussiness or difficulties with feeding.
What is Sandifer syndrome?
Sandifer syndrome (SS) is a movement disorder characterized by sudden spasms of the head, neck, and arching of the back, but does not affect the limbs. It is commonly linked to gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) in children.
Emily Mcmelon is a highly skilled and accomplished writer specializing in the field of pediatrics. With a deep passion for children’s health, she has dedicated her career to creating informative and engaging content that helps parents and caregivers navigate the complex world of pediatric care.