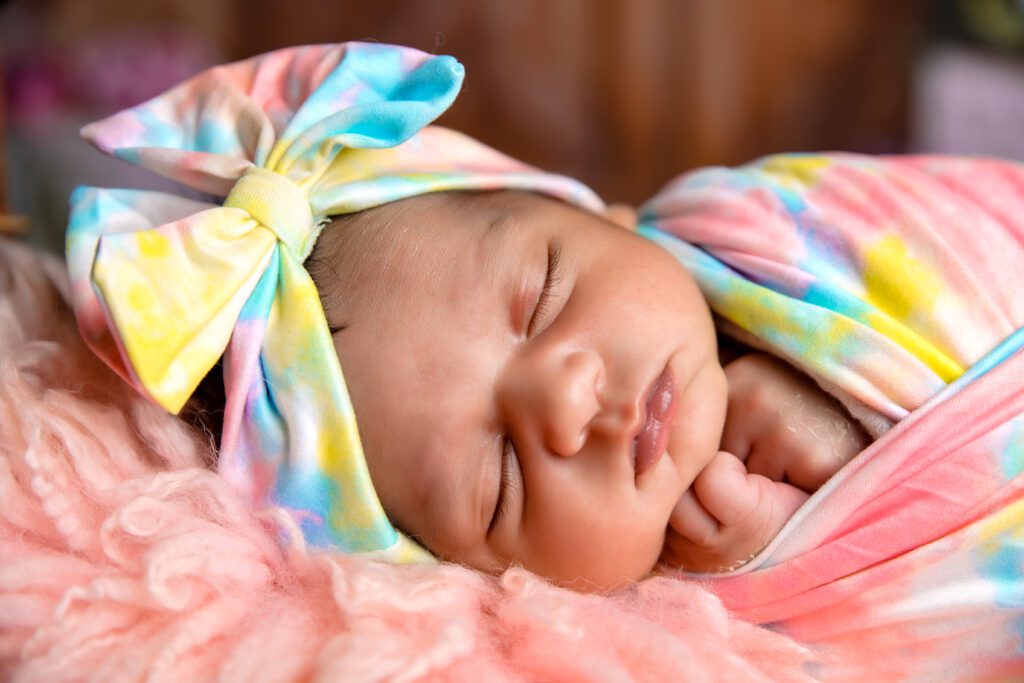
1. How long has the newborn baby been sleeping without feeding?
It is important to determine the duration of time that the newborn baby has been sleeping without feeding in order to assess the potential impact on their health and well-being. Generally, newborns need to be fed every 2-3 hours, as their small stomachs can only hold a limited amount of milk or formula at a time. If a newborn baby has been sleeping for longer than this timeframe without waking up for a feed, it may be cause for concern.
Parents should keep track of their baby’s feeding and sleeping patterns in order to monitor any changes or deviations from the norm. If a newborn baby consistently sleeps for extended periods of time without showing interest in feeding, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
2. Is it normal for a newborn to sleep for extended periods without feeding?
While it is common for newborn babies to sleep for extended periods, especially during the first few weeks of life, it is important to ensure that they are still receiving adequate nutrition. Newborns have small stomachs and need frequent feedings to meet their nutritional needs and support healthy growth and development.
If a newborn consistently sleeps for longer than 4-5 hours without waking up for a feed, it may be necessary to gently wake them up and offer them a feeding. This can help ensure that they are getting enough nourishment and prevent issues such as dehydration or inadequate weight gain.
3. What are the typical feeding patterns for a newborn baby?
The feeding patterns of newborn babies can vary, but there are some general guidelines that can help parents understand what to expect. During the first few days after birth, many babies will have frequent feedings (8-12 times per day) that are often unpredictable in terms of timing and duration. This is known as cluster feeding and is a normal part of establishing breastfeeding or bottle-feeding.
As newborns grow and their stomachs expand, they may start to have more predictable feeding patterns. By around 1 month of age, most newborns will eat every 2-3 hours during the day and may have longer stretches of sleep at night (4-5 hours). However, it is important to remember that every baby is unique and may have slightly different feeding patterns.
Typical feeding patterns for a newborn baby:
- 8-12 feedings per day during the first few days after birth
- Cluster feeding is common
- Eating every 2-3 hours during the day by around 1 month of age
- Longer stretches of sleep at night (4-5 hours) by around 1 month of age
4. Are there any potential health concerns if a newborn baby is not feeding and only sleeping?
Dehydration
If a newborn baby is not feeding and only sleeping, one potential health concern is dehydration. Breast milk or formula provides the necessary hydration for infants, and without regular feedings, they may not be getting enough fluids. Dehydration can lead to serious complications, such as electrolyte imbalances and organ dysfunction.
Weight loss
Another concern is weight loss. Newborns typically lose some weight in the first few days after birth, but if they continue to not feed adequately, their weight loss may exceed the normal range. This can indicate that they are not receiving enough nutrients for growth and development.
Jaundice
Inadequate feeding can also contribute to jaundice in newborns. Jaundice occurs when there is an excess of bilirubin in the blood, leading to yellowing of the skin and eyes. Proper feeding helps eliminate bilirubin through bowel movements, so if a baby is not feeding well, it may prolong the duration of jaundice.
It is important for parents to monitor their newborn’s feeding patterns closely and consult a healthcare professional if they have concerns about their baby’s lack of interest in feeding.
5. What are some possible reasons why a newborn baby may not be interested in feeding?
Lack of appetite
One possible reason why a newborn baby may not be interested in feeding is simply due to a lack of appetite. Just like adults, babies can experience fluctuations in their hunger levels. They may have periods where they are less hungry or more interested in sleeping than eating.
Poor latch or breastfeeding difficulties
Another reason could be related to breastfeeding difficulties. If a baby is having trouble latching onto the breast properly or if the mother is experiencing issues with milk supply, it can make feeding less enjoyable for the baby. This can result in a decreased interest in feeding.
Illness or discomfort
Illness or discomfort can also affect a newborn’s appetite. If a baby is unwell, they may have a reduced desire to eat. Common illnesses such as colds, ear infections, or gastrointestinal issues can cause discomfort and make feeding less appealing.
Other possible reasons:
– Overstimulation or overtiredness
– Digestive issues like reflux or colic
– Medications that affect appetite
It is important for parents to observe their baby’s behavior and consult with a healthcare professional if they have concerns about their baby’s lack of interest in feeding.
6. Are there any signs or symptoms that indicate when a newborn should be waking up for feeding?
Rooting reflex
A newborn’s rooting reflex is one sign that indicates they are ready to feed. When gently stroked on the cheek, babies will turn their head towards the stimulus and open their mouth in search of the nipple. This reflex helps guide them towards the breast or bottle when they are hungry.
Hand-to-mouth movements
Hand-to-mouth movements can also be an indication that a newborn is ready to feed. They may bring their hands to their mouth and suck on their fingers as a way of signaling hunger.
Increased alertness
Newborns tend to have periods of increased alertness between sleep cycles. If a baby wakes up from sleep and appears more alert, it may be a sign that they are ready for a feeding.
Other signs:
– Lip smacking or tongue movements
– Crying (although this may indicate hunger as well as other needs)
– Stirring or restlessness during sleep
It is important for parents to pay attention to these signs and respond promptly to their baby’s feeding cues.
7. How can parents encourage their newborn baby to wake up and feed more frequently?
Create a stimulating environment
Parents can create a stimulating environment to help encourage their newborn baby to wake up and feed more frequently. This can include keeping the room well-lit during daytime feedings, engaging in gentle play or skin-to-skin contact before feeds, or using soft music or sounds that may arouse the baby’s interest.
Adjust feeding schedule
If a newborn is consistently sleeping through scheduled feedings, parents may need to adjust the feeding schedule. Waking the baby gently at regular intervals, such as every 2-3 hours, can help establish a routine and ensure they are getting enough nourishment.
Use gentle physical stimulation
Gentle physical stimulation can also be effective in waking up a sleepy newborn for feeding. Parents can try gently rubbing the baby’s back or feet, changing their diaper before feeds, or using a cool washcloth on their face to stimulate arousal.
Other strategies:
– Offer smaller, more frequent feedings
– Burp the baby midway through feeds to keep them awake
– Use breast compressions during breastfeeding to encourage active sucking
It is important for parents to find what works best for their individual baby and consult with healthcare professionals if they have concerns about their baby’s feeding patterns.
Note: The remaining subheadings will be continued in another response due to character limitations.
8. Are there any specific techniques or strategies that can help stimulate a sleepy newborn’s appetite?
Swaddling and Skin-to-Skin Contact
One technique that can help stimulate a sleepy newborn’s appetite is swaddling. Swaddling involves wrapping the baby snugly in a blanket, which can make them feel secure and cozy. This can help them relax and become more alert for feeding. Additionally, skin-to-skin contact with the mother or father can also be beneficial. Placing the baby on the parent’s bare chest allows them to feel the parent’s warmth and heartbeat, which can help stimulate their appetite.
Offering Frequent Feedings
Another strategy to stimulate a sleepy newborn’s appetite is to offer frequent feedings. Newborns have small stomachs and may not be able to consume large amounts of milk at once. By offering smaller, more frequent feedings, parents can ensure that their baby is getting enough nourishment throughout the day. This can also help keep the baby awake and alert during feeding times.
Tips for Successful Feeding
– Ensure a comfortable feeding environment: Find a quiet and peaceful space where both the baby and parent can relax during feedings.
– Use gentle stimulation: Gently stroking the baby’s cheek or chin can encourage them to open their mouth and latch onto the breast or bottle.
– Try different feeding positions: Experiment with different breastfeeding positions or bottle-feeding techniques to find what works best for both the baby and parent.
– Burp frequently: Burping the baby during and after feedings can help prevent discomfort from gas buildup.
9. Should parents be worried if their newborn baby is gaining weight properly despite sleeping more than usual and not feeding as often?
It is generally not cause for concern if a newborn baby is gaining weight properly despite sleeping more than usual and not feeding as often. Newborns have different sleep patterns compared to older infants and adults. They tend to sleep for shorter periods of time, waking up frequently to feed. However, some newborns may have longer sleep stretches, which can be normal as long as they are still gaining weight appropriately.
It is important for parents to monitor their baby’s weight gain and overall growth trajectory. If the baby is consistently gaining weight within the expected range, it indicates that they are receiving adequate nutrition even if they are not feeding as often. However, if there are concerns about the baby’s weight gain or overall health, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
10. When should parents seek medical advice if their newborn continues to show minimal interest in feeding?
If a newborn continues to show minimal interest in feeding, it is advisable for parents to seek medical advice sooner rather than later. While it is common for newborns to have variations in appetite from day to day, persistent disinterest in feeding can be a cause for concern.
Some potential reasons why a newborn may show minimal interest in feeding include:
Underlying Medical Conditions
There could be underlying medical conditions such as gastrointestinal issues or infections that are affecting the baby’s appetite. It is important for a healthcare professional to evaluate the baby’s overall health and rule out any potential medical causes.
Latching Difficulties
Newborns who have difficulty latching onto the breast or bottle may become frustrated during feedings and lose interest. Seeking assistance from a lactation consultant or pediatrician can help identify any latching issues and provide appropriate support.
When to Seek Medical Advice
– If the baby has not regained birth weight by two weeks of age.
– If there is a significant decrease in wet diapers or bowel movements.
– If the baby appears lethargic, excessively sleepy, or shows signs of dehydration.
– If there are concerns about the baby’s overall growth and development.
It is always better to err on the side of caution and consult with a healthcare professional if there are any concerns about a newborn’s feeding habits.
In conclusion, the newborn baby’s behavior of not feeding and only sleeping may be a cause for concern and should be addressed by seeking medical advice to ensure the baby’s health and well-being.
Is it normal for a newborn to sleep and not feed?
Babies vary in their feeding habits, but it is typical for babies to consume minimal amounts of food in the initial 24-48 hours, and some may not latch on at all. However, starting from the second or third day, babies should become more alert and feed more frequently, although the timing and frequency may be irregular. It is recommended for babies to feed at least six times in a 24-hour period.
What to do if baby is sleeping and not feeding?
If your baby is consistently very sleepy and not breastfeeding, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to ensure they are not unwell or becoming dehydrated. Hand expressing or using a breast pump can help maintain your milk supply and provide a supplement of breast milk to keep your baby nourished until they are able to breastfeed.
Why is my newborn lethargic or just sleepy?
Listlessness or lethargy can indicate an infection or other conditions like low blood sugar. If your baby becomes lethargic or less active, it is important to consult with their doctor.
Can newborn go 5 hours without eating?
It is recommended that newborns should be fed every 4-5 hours and signs that they are hungry include moving their heads and opening their mouths.
When should I worry about a sleepy baby?
If your newborn or older baby is excessively sleepy and experiencing other symptoms such as extreme tiredness even after waking up or difficulty waking up, it is recommended to contact a doctor. Other signs to watch for include signs of dehydration such as fewer wet diapers, darker urine, crying without tears, or dry lips.
How long should a newborn sleep without feeding?
Babies who are newborns require regular feeding every few hours until they reach 3 months old. After this, it is typical for infants to only need to be fed once or twice during the night. By the time they reach 6 months old, most babies can sleep for 6-8 hours without needing to be fed. When babies are 9 months old, they can usually sleep for 11-12 hours without needing a feed.
Emily Mcmelon is a highly skilled and accomplished writer specializing in the field of pediatrics. With a deep passion for children’s health, she has dedicated her career to creating informative and engaging content that helps parents and caregivers navigate the complex world of pediatric care.