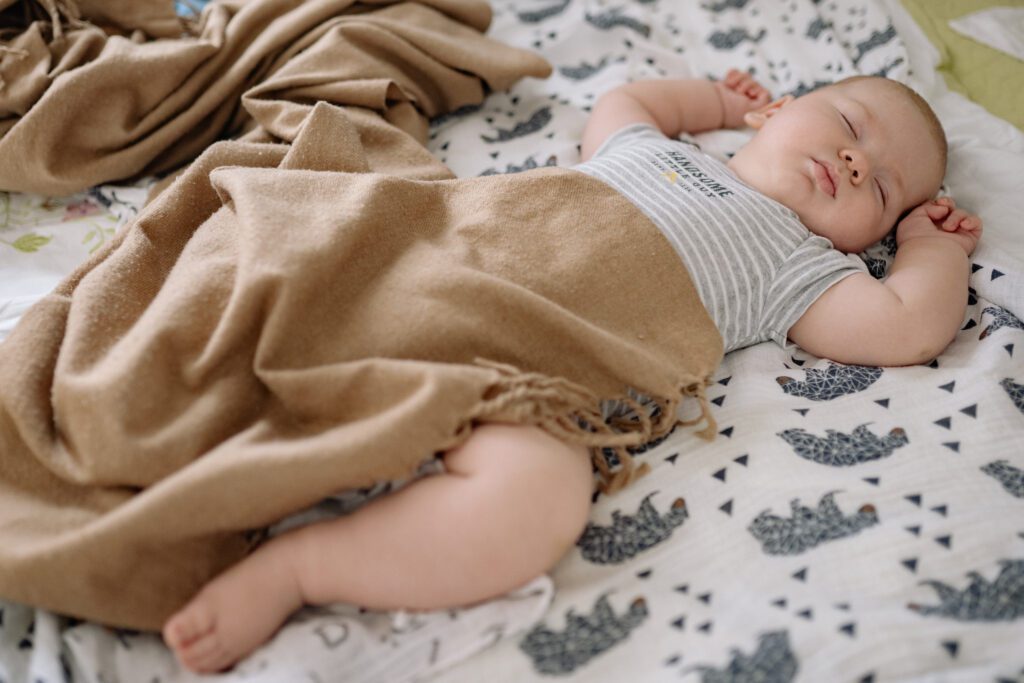
1. At what age do babies typically start rolling their eyes back when sleeping?
Rolling the eyes back during sleep is a common behavior in infants, and it typically starts around 3 to 4 months of age. At this stage, babies have gained more control over their eye muscles and are able to move their eyes independently. As they enter the REM (rapid eye movement) phase of sleep, which is when most dreaming occurs, their eyes may roll back or dart rapidly from side to side.
It’s important to note that every baby develops at their own pace, so some infants may start rolling their eyes back earlier or later than others. Additionally, premature babies may exhibit this behavior slightly later due to their adjusted developmental timeline.
Factors that can influence eye rolling:
- Physical development: Eye rolling during sleep is linked to the maturation of the ocular muscles and nervous system.
- Sleep patterns: The frequency and duration of REM sleep cycles can affect how often a baby’s eyes roll back during sleep.
- Dreaming activity: Eye movements during sleep are associated with dreaming, so increased brain activity during REM sleep can lead to more pronounced eye rolling.
Tips for parents:
If your baby has not started rolling their eyes back by 6 months of age or if you have any concerns about their eye movements during sleep, it’s best to consult with a pediatrician or an ophthalmologist for further evaluation and guidance.
2. Is it normal for a baby’s eyes to roll back during sleep?
Yes, it is completely normal for a baby’s eyes to roll back during sleep. It is a natural part of the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep, which is when most dreaming occurs. During REM sleep, the brain is highly active, and the eyes move rapidly in different directions. This movement can sometimes cause the eyes to roll back or dart rapidly from side to side.
While it may look concerning to parents, especially if they are witnessing it for the first time, eye rolling during sleep is generally not a cause for alarm. It is a normal physiological response and does not indicate any underlying health issues.
Reasons for eye rolling during sleep:
- Brain activity: Eye movements during REM sleep are believed to be linked to the brain’s processing of information and consolidation of memories.
- Muscle development: Rolling the eyes back during sleep helps strengthen and coordinate the muscles responsible for eye movement.
- Eye protection: Rolling the eyes back during sleep helps protect the delicate cornea by keeping it moist with tears.
Tips for parents:
If your baby’s eyes roll back occasionally while sleeping and they are otherwise healthy and meeting their developmental milestones, there is usually no cause for concern. However, if you notice any other unusual symptoms or have concerns about your baby’s eye health, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
3. Why do some babies’ eyes roll back while they are asleep?
Causes of eye rolling during sleep
There can be several reasons why a baby’s eyes may roll back while they are asleep. One common cause is the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep, which is when most dreaming occurs. During this phase, the eyes may move in various directions, including rolling back. Another possible cause is the immaturity of the baby’s visual system. Babies are born with underdeveloped eye muscles and coordination, so their eye movements during sleep may appear more exaggerated or erratic compared to adults.
Additionally, certain medical conditions or medications can also contribute to eye rolling during sleep in babies. For example, infants with seizure disorders may experience abnormal eye movements as part of their seizures. It’s important for parents to consult with a healthcare professional if they have concerns about their baby’s eye rolling during sleep.
Tips for parents:
- Observe your baby’s sleeping patterns and note if there are any specific triggers or patterns associated with their eye rolling.
- Keep a record of when and how frequently your baby’s eyes roll back during sleep to provide accurate information to healthcare professionals.
- If you suspect a medical condition or medication side effect may be causing the eye rolling, discuss your concerns with your pediatrician or a specialist.
4. Are there any potential health concerns associated with a baby’s eyes rolling back during sleep?
In most cases, occasional eye rolling during sleep is considered normal and not a cause for concern. However, it is essential for parents to be aware of any potential underlying health issues that could be contributing to excessive or concerning eye behavior in their baby.
One potential health concern associated with eye rolling during sleep is the presence of seizures. Seizures can manifest as abnormal eye movements, including rolling back or fluttering. If a baby’s eye rolling is accompanied by other seizure symptoms such as jerking movements, loss of consciousness, or changes in breathing patterns, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Other possible health concerns related to eye rolling during sleep include neurological disorders or visual impairments. If parents notice consistent and persistent eye rolling that does not seem to be within the normal range of movement, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
5. How can parents differentiate between normal eye movement during sleep and concerning eye behavior in babies?
Observation and Comparison
Parents can differentiate between normal eye movement during sleep and concerning eye behavior in babies by observing and comparing their baby’s eye movements to typical patterns. Normal eye movement during sleep includes rapid eye movements (REM) and occasional fluttering or rolling of the eyes. These movements are a part of the natural sleep cycle and are usually accompanied by other signs of deep sleep, such as relaxed muscles and regular breathing.
Signs of Concern
However, if parents notice any unusual or excessive eye movements that seem different from the typical patterns, it may be a cause for concern. Some signs to look out for include sustained or repetitive rolling of the eyes, eyes crossing or turning inward excessively, or eyes remaining fixed in one position for an extended period. If these behaviors persist or are accompanied by other abnormal symptoms like seizures, delayed development, or difficulty feeding, it is important to consult a pediatrician for further evaluation.
6. Can excessive eye rolling during sleep indicate a neurological issue in infants?
Excessive eye rolling during sleep can sometimes indicate a neurological issue in infants. While occasional eye rolling is considered normal during REM sleep, persistent or frequent episodes of excessive eye rolling may be a sign of an underlying neurological condition. Neurological issues that can cause abnormal eye movements include infantile spasms, seizures, nystagmus (involuntary rhythmic oscillations of the eyes), or developmental disorders affecting the brain.
It is essential for parents to pay attention to other accompanying symptoms such as delayed milestones, poor muscle tone, abnormal reflexes, irritability, or changes in feeding patterns. If there are concerns about excessive eye rolling or any other unusual behaviors during sleep, it is crucial to seek medical advice from a pediatrician or a pediatric neurologist for a thorough evaluation and appropriate diagnosis.
7. Are there any specific factors that may trigger eye rolling in babies while they are asleep?
There can be specific factors that may trigger eye rolling in babies while they are asleep. These triggers can vary from individual to individual, but some common factors include:
1. Dreams and Sleep Cycles: Eye movements during sleep, including rolling, are often associated with the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of the sleep cycle. During this phase, babies may experience vivid dreams or active brain activity, leading to various eye movements.
2. Sensory Stimulation: Certain sensory stimuli such as bright lights, loud noises, or sudden movements can cause babies to have reflexive eye movements during sleep, including rolling.
3. Discomfort or Pain: Babies who are experiencing discomfort or pain due to teething, digestive issues, or illness may exhibit increased eye rolling during sleep as their body tries to find a more comfortable position.
It is important for parents to observe their baby’s behavior and environment to identify any potential triggers for excessive eye rolling during sleep. If certain triggers are identified, parents can try minimizing or eliminating them to see if it reduces the frequency of eye rolling episodes.
8. Do all babies experience eye rolling to some extent during sleep, or is it more common in certain individuals?
Eye rolling during sleep is a normal phenomenon experienced by most babies to some extent. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is an essential part of the sleep cycle for infants and adults alike. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly in different directions, which can include occasional fluttering or rolling of the eyes.
However, the frequency and intensity of eye rolling can vary among individuals. Some babies may exhibit more noticeable and frequent eye movements during REM sleep compared to others. It is also worth noting that premature infants tend to have more eye movements during sleep than full-term babies.
While occasional eye rolling is considered normal, persistent or excessive eye rolling that interferes with sleep or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Every baby is unique, and it is important for parents to trust their instincts and seek medical advice if they have any concerns about their baby’s eye movements during sleep.
9. What should parents do if they notice their baby’s eyes frequently rolling back while sleeping?
If parents notice their baby’s eyes frequently rolling back while sleeping, it is important to take certain steps:
1. Observe and Document: Parents should carefully observe and document the frequency, duration, and any accompanying symptoms of the eye rolling episodes. This information will be helpful when discussing concerns with a healthcare professional.
2. Consult a Pediatrician: It is recommended to consult a pediatrician if the eye rolling episodes are persistent, frequent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as delayed development, seizures, or difficulty feeding. The pediatrician can conduct a thorough examination and determine whether further evaluation by a specialist, such as a pediatric neurologist, is necessary.
3. Follow Medical Advice: If a healthcare professional identifies any underlying issues or concerns related to the frequent eye rolling episodes during sleep, they will provide appropriate guidance and treatment options. It is crucial for parents to follow the recommended medical advice and attend any follow-up appointments as needed.
By seeking medical attention and following professional advice, parents can ensure that any potential underlying causes of frequent eye rolling in their baby are properly addressed.
10. Are there any strategies or techniques parents can use to prevent or minimize eye rolling during their baby’s sleep?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent or control all instances of eye rolling during a baby’s sleep, there are some strategies that parents can try:
1. Create a Calm Sleep Environment: Establishing a soothing sleep environment can help promote better sleep and potentially reduce eye rolling. This includes keeping the room dark, maintaining a comfortable temperature, and minimizing noise or distractions.
2. Consistent Bedtime Routine: Implementing a consistent bedtime routine can signal to the baby that it is time to sleep. This routine may include activities such as a warm bath, gentle massage, reading a book, or singing lullabies. A predictable routine can help relax the baby and potentially minimize eye rolling.
3. Address Discomfort or Pain: If discomfort or pain is suspected as a trigger for eye rolling during sleep, parents should address these issues promptly. This may involve providing appropriate pain relief measures for teething discomfort or consulting a healthcare professional for guidance on managing any underlying medical conditions.
4. Consult with Healthcare Professionals: If eye rolling episodes persist despite trying various strategies, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals for further evaluation and guidance. They may recommend additional interventions or refer to specialists if necessary.
It is essential for parents to remember that every baby is different, and what works for one may not work for another. Patience and open communication with healthcare professionals are key in finding the most suitable strategies to minimize eye rolling during their baby’s sleep.
In conclusion, it is common for babies’ eyes to roll back when they are sleeping.
Is it normal for babies to roll eyes back when falling asleep?
They are attempting to understand how to manage their eye movements and develop the ability to concentrate on objects. Additionally, it is normal for a baby to roll their eyes while sleeping or when they are in the process of falling asleep or waking up.
When do babies eyes stop rolling back?
It is common for a newborn’s eyes to occasionally wander or cross in the first few months of life. However, by the time a baby is 4-6 months old, their eyes typically align correctly. If one or both eyes continue to wander in different directions, it is likely due to a condition called strabismus.
What does it mean when a child’s eyes roll back?
Tonic-clonic seizures begin with the child being unaware of their surroundings and possibly making a strange noise. The first stage of the seizure is called the tonic phase, during which the entire body becomes rigid and the eyes may roll back or to the side.
Why do babies open and roll their eyes while sleeping?
The combination of a developing nervous system and REM sleep patterns may be the reason why babies often have their eyes open during sleep. Babies experience longer periods of REM sleep compared to adults, and both adults and babies exhibit more eye movement during REM sleep. This phenomenon is believed to be influenced by their still-developing nervous system.
What does a seizure in a baby look like?
More noticeable indications may involve the infant’s arms rising with a subtle nod of the head and their eyes rolling upwards. Although these movements may appear as if the baby is simply startled, spasms can happen in clusters lasting for several minutes, with each spasm lasting five to ten seconds, when the baby is just waking up or preparing to sleep.
Can eye rolling be a seizure?
Eyelid myoclonia is the most prevalent form of seizures, characterized by brief and recurring jerks of the eyelids. The eyeballs may roll upwards, and there could be a slight backward movement of the head. These episodes typically endure for less than 6 seconds but can occur multiple times throughout the day.
Emily Mcmelon is a highly skilled and accomplished writer specializing in the field of pediatrics. With a deep passion for children’s health, she has dedicated her career to creating informative and engaging content that helps parents and caregivers navigate the complex world of pediatric care.