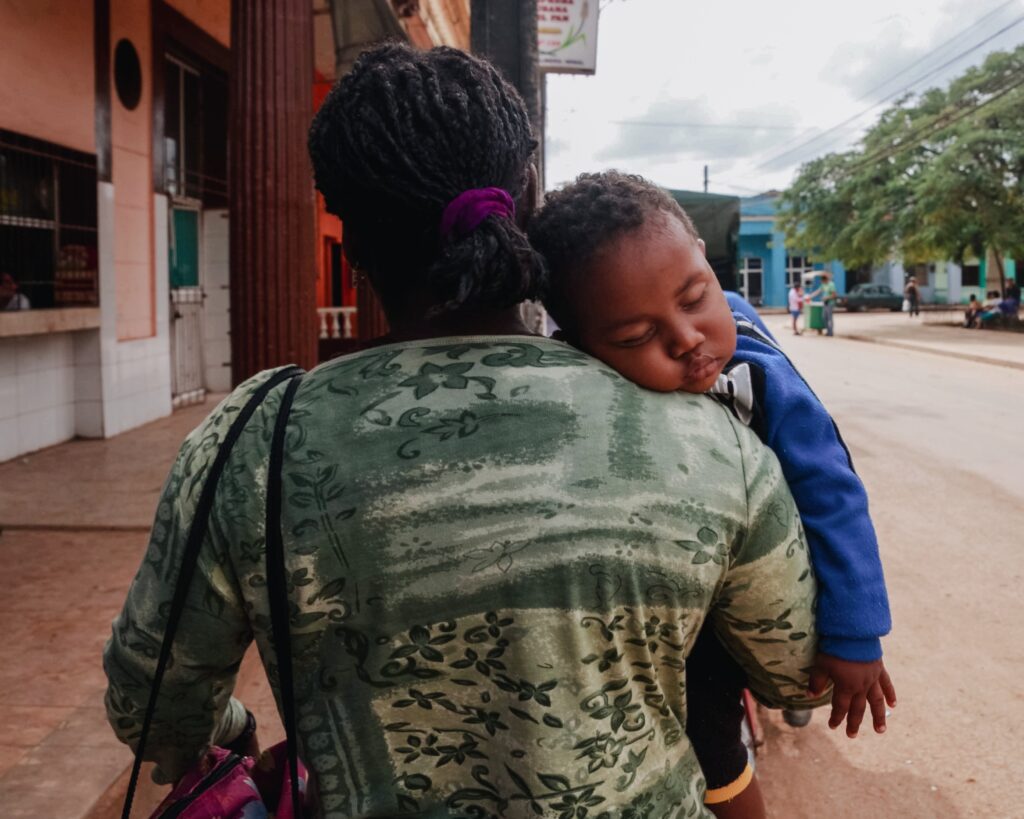
Common Reasons for a Baby to Stop Breathing Momentarily While Sleeping
There are several common reasons why a baby may stop breathing momentarily while sleeping. One of the most common causes is sleep apnea, which is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. Sleep apnea can occur due to obstructions in the airway, such as enlarged tonsils or adenoids. Another common cause is reflux, where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus and can cause brief pauses in breathing. Additionally, immature respiratory control centers in the brain can also contribute to breathing pauses during sleep.
H3: Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a condition that causes repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. It occurs when the muscles in the throat relax and block the airway, leading to brief pauses in breathing. This can result in snoring, gasping, or choking sounds as the baby tries to resume normal breathing. Sleep apnea can be caused by factors such as obesity, enlarged tonsils or adenoids, or structural abnormalities in the airway.
H3: Reflux
Reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. In some cases, this reflux can lead to brief pauses in breathing during sleep. The acid irritates the lining of the esophagus and can trigger a reflex that temporarily stops breathing. Reflux is more common in infants due to their underdeveloped digestive systems.
Immature Respiratory Control Centers
Babies have immature respiratory control centers in their brains, which means they may have difficulty regulating their breathing patterns during sleep. This immaturity can result in occasional pauses in breathing while sleeping. As babies grow and develop, these control centers become more mature and breathing becomes more regular.
Duration Considered Normal for a Baby to Pause Breathing During Sleep
It is normal for babies to have brief pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses are known as periodic breathing and typically last for a few seconds. Periodic breathing is more common in premature infants but can occur in full-term babies as well. During these pauses, the baby may appear to stop breathing or take shallow breaths. However, they will usually resume normal breathing on their own without any intervention.
H3: Premature Infants
Premature infants are more likely to experience periodic breathing and may have longer pauses in their breathing compared to full-term babies. This is because their respiratory control centers are still developing and may not be fully matured. It is important for healthcare providers to monitor premature infants closely during sleep to ensure that their breathing patterns remain within a safe range.
Full-Term Babies
Even full-term babies can experience periodic breathing, although it is generally less frequent and shorter in duration compared to premature infants. It is considered normal for a baby to pause their breathing for up to 10-15 seconds during sleep. If the pauses become longer or more frequent, it may be a cause for concern and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Warning Signs and Symptoms Indicating a More Serious Issue When a Baby Stops Breathing While Sleeping
While brief pauses in breathing during sleep are generally considered normal, there are certain warning signs and symptoms that may indicate a more serious underlying issue when a baby stops breathing while sleeping. These warning signs include:
- Cyanosis: Bluish discoloration of the skin or lips
- Excessive daytime sleepiness or difficulty staying awake
- Frequent awakenings from sleep accompanied by gasping or choking sounds
- Poor weight gain or failure to thrive
- Severe snoring or noisy breathing
If a baby exhibits any of these warning signs, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition such as sleep apnea, respiratory distress, or a neurological disorder.
Immediate Actions Parents Should Take if Their Baby Stops Breathing During Sleep
If a parent notices that their baby has stopped breathing during sleep, it is important to remain calm and take immediate action. The following steps should be taken:
- Gently stimulate the baby: Gently touch or stroke the baby to try and elicit a response. Sometimes, babies may have brief pauses in breathing but can be easily aroused and resume normal breathing on their own.
- Call for emergency medical assistance: If the baby does not respond or resumes breathing but appears distressed, it is important to call for emergency medical assistance immediately.
- Perform infant CPR if necessary: If the baby remains unresponsive and is not breathing, begin infant CPR following the appropriate guidelines. This can help maintain oxygen flow until medical professionals arrive.
It is important for parents to learn infant CPR techniques and have knowledge of emergency procedures in case of such situations. Taking an infant CPR course can provide parents with the necessary skills and confidence to handle emergencies effectively.
Should You Wake Up a Baby Who Has Briefly Stopped Breathing While Sleeping?
Understanding the Normal Breathing Patterns of Babies
Babies have different breathing patterns compared to adults. It is common for them to have irregular breathing, including brief pauses or periods of shallow breathing while they sleep. These pauses can last for a few seconds and are usually harmless. In fact, waking up a baby who has briefly stopped breathing may disrupt their sleep and cause unnecessary stress. However, it is important to differentiate between normal breathing patterns and more serious conditions that require medical attention.
Signs That Indicate the Need for Medical Assistance
While brief pauses in breathing are generally normal, there are certain signs that indicate a need for medical assistance. If your baby’s lips or face turn blue, if they appear limp or unresponsive, or if they have prolonged periods of not breathing, it is crucial to seek immediate medical help. These symptoms could be indicative of a more serious condition such as sleep apnea or other respiratory disorders.
Precautions to Take
To ensure your baby’s safety during sleep, there are some precautions you can take. Firstly, always place your baby on their back to sleep as this reduces the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Additionally, avoid exposing your baby to secondhand smoke as it can increase the chances of respiratory problems. Keep the sleeping environment free from hazards such as loose bedding or stuffed animals that could obstruct their airway.
It is essential to stay informed about normal breathing patterns in babies and be aware of any signs that may indicate a need for medical assistance. By taking necessary precautions and seeking appropriate help when needed, you can ensure your baby’s well-being during sleep.
Sleep Positions That Increase the Risk of a Baby Temporarily Ceasing to Breathe During Sleep
The Importance of Safe Sleep Positions
The sleep position of a baby plays a crucial role in their breathing and overall safety during sleep. Certain sleep positions can increase the risk of a baby temporarily ceasing to breathe, which can be dangerous. It is important for parents and caregivers to be aware of these positions and take necessary precautions.
Risk Factors Associated with Prone Sleeping Position
The prone sleeping position, where the baby lies on their stomach, has been associated with an increased risk of breathing difficulties. This position can potentially obstruct the airway and lead to temporary cessation of breathing. It is recommended to avoid placing babies in this position to reduce the risk.
Safe Sleep Positions
To minimize the risk of a baby temporarily ceasing to breathe during sleep, it is advised to place them on their back. The supine sleeping position, where the baby lies on their back, is considered the safest for sleep. This position allows for proper airflow and reduces the likelihood of obstruction or apnea episodes.
By understanding the importance of safe sleep positions and avoiding prone sleeping, parents can significantly reduce the chances of their baby experiencing breathing pauses during sleep.
(Note: Always follow safe sleep guidelines provided by healthcare professionals or organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics.)
Please note that this response provides general information and should not substitute professional medical advice. If you have concerns about your baby’s breathing patterns or any other health-related issues, consult with a healthcare provider.
Preventive Measures to Reduce the Chances of a Baby Experiencing Breathing Pauses While Asleep
Creating a Safe Sleeping Environment
It is important to create a safe sleeping environment for your baby to reduce the chances of breathing pauses while asleep. This includes placing your baby on their back to sleep, as this position has been shown to decrease the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Make sure the crib or bassinet is free from any loose bedding, pillows, or stuffed animals that could potentially obstruct your baby’s airway. Keep the room at a comfortable temperature and avoid overdressing your baby, as overheating can also increase the risk of breathing difficulties during sleep.
Monitoring Your Baby’s Sleep Position and Breathing Patterns
Regularly monitoring your baby’s sleep position and breathing patterns can help identify any potential issues early on. Use a reliable baby monitor with video and audio capabilities to keep an eye on your little one while they sleep. This can provide reassurance and allow you to quickly respond if you notice any irregularities in their breathing or if they experience pauses in their breathing. Additionally, consider using a movement monitor that detects even subtle movements such as breathing movements. These monitors can alert you if there are prolonged periods without movement, giving you peace of mind.
When to Seek Medical Assistance if Your Baby Frequently Stops Breathing While Sleeping
If your baby frequently stops breathing while sleeping, it is crucial to seek medical assistance promptly. While occasional pauses in breathing may be normal for some babies, frequent or prolonged episodes could indicate an underlying medical condition that requires evaluation and treatment by a healthcare professional.
Signs That Require Immediate Medical Attention
If your baby turns blue or pale during episodes of paused breathing, appears limp or unresponsive, or has difficulty waking up after these episodes, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention. These signs could indicate a more severe condition that requires urgent intervention.
Consulting with Your Pediatrician
If you notice frequent pauses in your baby’s breathing during sleep, it is advisable to consult with your pediatrician. They can evaluate your baby’s overall health and conduct a thorough examination to determine the underlying cause of the breathing pauses. Your pediatrician may also recommend further tests or refer you to a specialist for further evaluation if necessary.
Medical Conditions or Disorders that Could Cause Intermittent Pauses in a Baby’s Breathing During Sleep
There are several medical conditions or disorders that could contribute to intermittent pauses in a baby’s breathing during sleep. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for appropriate management and treatment.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when there is a partial or complete blockage of the airway during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing. This condition can affect babies as well as older children and adults. Common causes of OSA in infants include enlarged tonsils or adenoids, craniofacial abnormalities, or neuromuscular disorders.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
Central sleep apnea is characterized by the brain failing to send proper signals to the muscles responsible for controlling breathing during sleep. This results in intermittent pauses in breathing. CSA can be caused by certain medical conditions such as congenital heart defects, neurological disorders, or premature birth.
Tests and Examinations Used to Determine the Underlying Cause When a Baby Stops Breathing Momentarily While Sleeping
When a baby stops breathing momentarily while sleeping, various tests and examinations may be conducted to determine the underlying cause.
Pulse Oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive test that measures the oxygen saturation level in your baby’s blood. It involves placing a small sensor on their skin, typically on their foot or hand. This test can help identify any potential issues with oxygen levels during sleep and provide valuable information for diagnosis.
Sleep Study (Polysomnography)
A sleep study, also known as polysomnography, is a comprehensive test that monitors various physiological parameters during sleep. It involves attaching sensors to your baby’s body to record brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, breathing patterns, and oxygen levels. This test can help determine if there are any abnormalities in your baby’s sleep patterns and identify the underlying cause of breathing pauses.
Consultation with Specialists
In some cases, consultation with specialists such as pediatric pulmonologists or pediatric neurologists may be necessary to further evaluate the underlying cause of breathing pauses during sleep. These specialists have expertise in diagnosing and managing respiratory or neurological conditions that could contribute to these episodes. They may recommend additional tests or treatments based on their evaluation.
In conclusion, it is crucial for parents and caregivers to remain vigilant and take necessary precautions to ensure the safety of babies while they sleep.
Why does my baby stop breathing then gasp for air?
If your baby frequently stops or pauses their breathing, or if they stop breathing for 20 seconds or longer, or if you notice any gasping, choking, snoring, coughing, or snorting sounds while they are sleeping, it is important to schedule an appointment with their doctor. These could all be indications of apnea.
What does baby sleep apnea sound like?
Instead of the typical snoring sound, you might hear a high-pitched noise known as “stridor.” The medical term for this condition, which is caused by a floppy or underdeveloped voice box, is laryngomalacia. While babies can have both laryngomalacia and OSA (obstructive sleep apnea), a sleep study is required to diagnose OSA.
Can sleep apnea cause SIDS?
Since OSA leads to increased levels of carbon dioxide and decreased levels of oxygen in the body, it is possible that an unusual reaction of infants to these conditions could contribute to SIDS.
What are 3 signs a baby is in respiratory distress?
Signs to look for include chest retractions, where the chest pulls in with each breath, particularly around the collarbone and ribs. Also check for nasal flaring, which is when the nostrils widen during inhalation. Listen for sounds like an “Ugh” sound, wheezing, or the sensation of mucus in the throat. Lastly, assess the child’s skin to see if it feels cool but also sweaty, indicating clamminess.
What are common signs of impending respiratory failure in infants?
If your child is experiencing symptoms of respiratory failure such as difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, bluish discoloration of the skin, lips, and fingernails (known as cyanosis), and confusion, it is important to seek medical evaluation from a doctor.
What is near miss SIDS?
Infants who were found seemingly lifeless and needed intense stimulation or mouth-to-mouth resuscitation to be revived were referred to as having a near-miss SIDS (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome).
Emily Mcmelon is a highly skilled and accomplished writer specializing in the field of pediatrics. With a deep passion for children’s health, she has dedicated her career to creating informative and engaging content that helps parents and caregivers navigate the complex world of pediatric care.