Motherhood, One Nap at a Time
Welcome to your digital village, where I share honest encouragement, researched baby tips, and the simple things that make the newborn days feel a little less overwhelming. Grab a cup of coffee (reheated is fine) and settle in—you’re doing a great job, mama.
Fresh Reads !
The latest tips, honest reviews, and parenting insights hot off the press. Dive into our newest articles covering everything from essential baby gear comparisons to practical advice for navigating the first years of parenthood.
Check Them Out!The Lifestyle Starter Bundle
Get my free Lifestyle Starter Bundle and jump into a curated mix of easy routines, home tips, wellness ideas, and gentle inspiration.
Grab the guide now!What’s trending
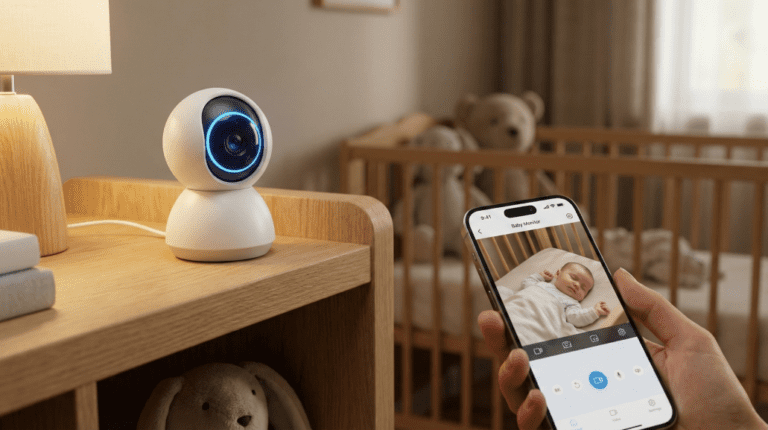
 Tech
Tech
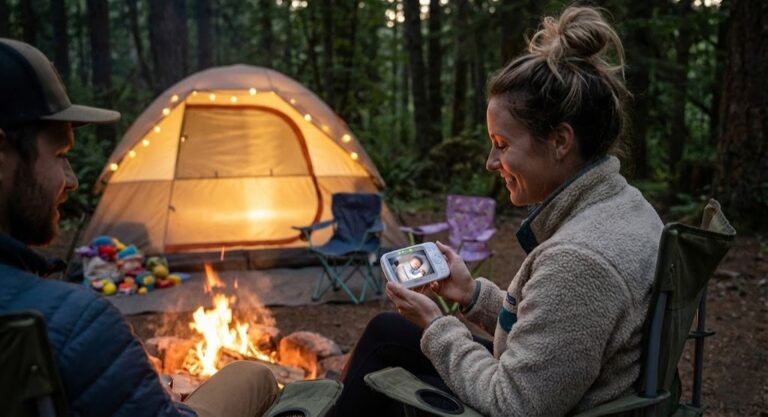
Best Camping Baby Monitor: Top Battery-Powered Picks 2026
Sitting by a crackling campfire is pure magic until you hear a suspicious rustling sound coming from the family tent. Is it a raccoon looking for marshmallows, or is your toddler trying to escape her sleeping bag? Finding a reliable camping baby monitor was the only way I could finally relax under the stars with…